- 12 May
- 2023
Ilustrasi gambar (freepik)
Child Syphilis Cases in Indonesia Increase 70%, UM Surabaya Lecturer Advises This
Recently, the Ministry of Health (Kemenkes) revealed the latest facts regarding cases of sexually transmitted diseases in Indonesia. Mohammad Syahril as a spokesperson for the Ministry of Health said that syphilis cases had increased by almost 70% in the last five years, namely from 2018 to 2022 yesterday.
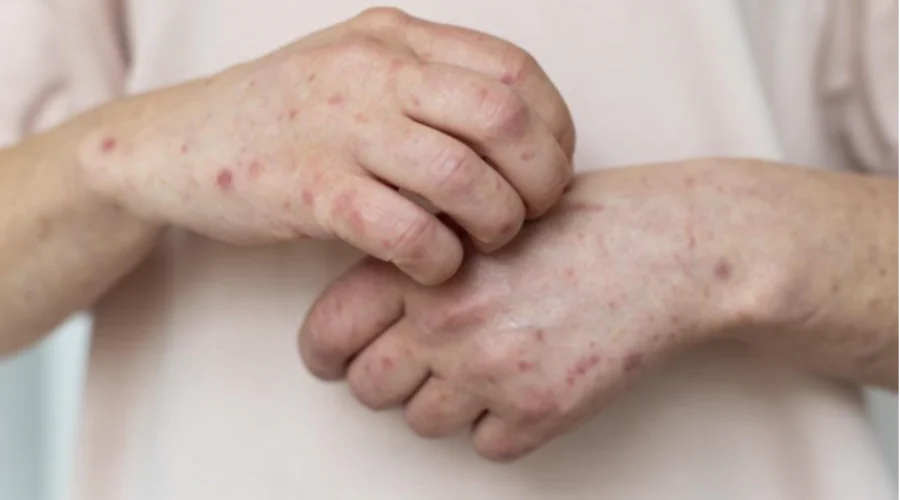
Syphilis or lion king disease is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by bacteria.
Syphilis, also known as lion king disease, is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum.
Idham Choliq, a lecturer at the Faculty of Health Sciences (FIK) UM Surabaya, said that syphilis can cause serious health effects if there is no adequate treatment.
According to him, the disease begins as a painless sore, usually on the genitals, rectum or mouth. If left untreated, this disease can damage the heart, brain or other organs, and can be life-threatening.
“Syphilis is spread from person to person through direct contact with syphilitic sores, known as chancres. Chancre can occur around the penis, vagina, anus, rectum, and lips or mouth," added Idham again.
Idham also said that syphilis can be spread during vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Pregnant people with syphilis can also pass the infection to their unborn children.
“The average time between contracting syphilis and the start of the first symptoms is 21 days. However, this can range from 10 to 90 days,” he stressed.
In his statement, Idham also shared tips to avoid syphilis.
First, loyal to one partner or monogamy. Idham emphasized that having a long-term monogamous relationship with a partner who does not suffer from syphilis is the only way to prevent syphilis.
Second, the use of condoms. Condoms when used correctly every time someone has sex can reduce the risk of getting or suffering from syphilis. Condoms offer protection when they cover the infected area or potential exposure. However, transmission of syphilis can occur with lesions not covered by a condom.
Third, avoid contact with people with syphilis. Avoiding syphilis is not having vaginal, anal, or oral sex with people with syphilis.









(0) Comments